Laser scanner: what is it, what are its functions, and what types are there?
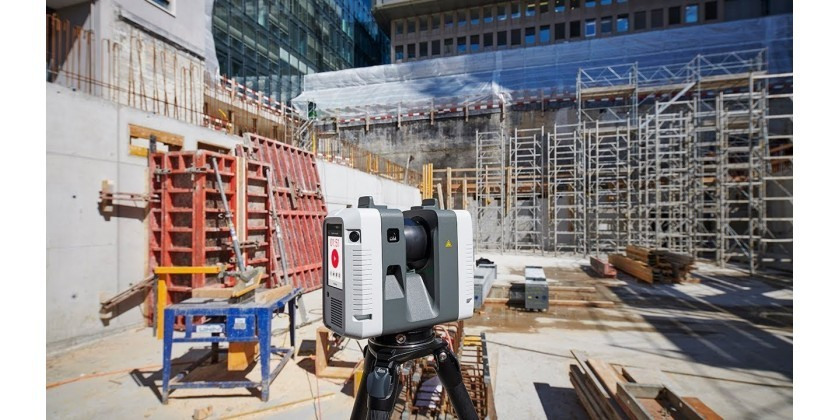

A laser scanner is one of the best-selling surveying instruments in our online surveying shop in recent years.
A laser scanner is one of the best-selling surveying instruments in our online surveying store. Whether it is for new projects, renovating a house, refurbishing a commercial space, or any other application, you will need to obtain accurate data. 3D scanning involves surveying a space using a 3D laser scanner to create point clouds. This cloud is made up of millions of points that meticulously recreate a space and its physical components.
In this post, we will try to delve deeper into this tool. We will tell you what a laser scanner is, what types of scanners exist, their uses, and the 3D scanner models available in the market.
We hope you find our article interesting! If so, stay tuned as we begin:
What is a laser scanner?
A terrestrial laser scanner, or simply a laser scanner, is an instrument used to capture the geometry and color of any object or the surrounding environment by collecting massive amounts of data. These data, in the form of point clouds, are obtained by measuring distances and angles using a laser beam of light, combined with cameras to capture visible range information. These data are then used to create a three-dimensional model of the object. In other words, with laser scanner technology, we can transform a real object into a virtual one and manipulate it through specialized software.
The potential of scanners is incredibly high, allowing for the acquisition of geographical coordinates of all surfaces surrounding the instrument (within a limited radius) in a matter of minutes, without any need for physical contact with the measured elements.
Now that we hae explained what a laser scanner is and what you can do with it, let's explore the different types of scanners available in the market.
Types of laser scanners
We can classify laser scanners based on distance measurement or collection technique. According to this distinction, we have:
Types of laser scanners based on distance measurement:
- Time of Flight: This technique relies on measuring the time it takes for the laser to travel from the emitter, reflect off the scanned object, and return to the receiver. This technique allows precise control of the laser's return time and the storage of multiple returns from a single pulse. Time of Flight laser scanners can cover long distances, making them highly useful in topography, where this increases productivity.
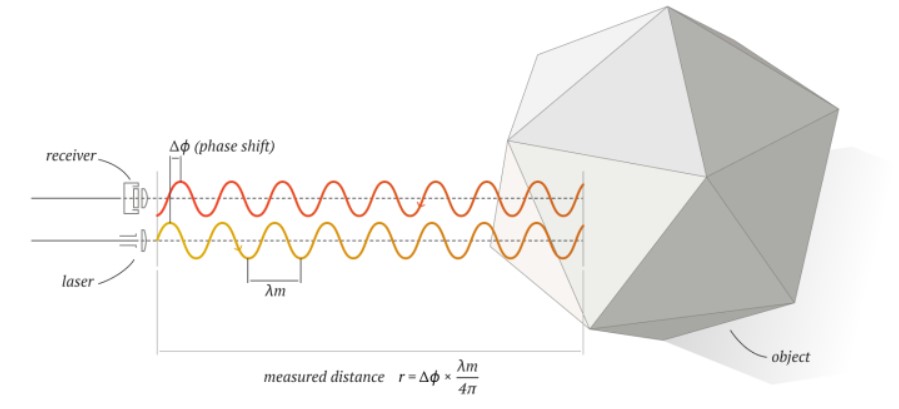
- Phase Shift: These laser scanners emit a series of laser waves with different wavelengths onto the measured object. When these waves are reflected and received by the scanner, they allow the determination of the object's distance by comparing the phase of emitted and received waves. The major advantage of this technique is higher measurement precision (down to tenths of a millimeter in distance) and the number of points recorded, which can reach up to 1 million points per second. These laser measurement systems are widely used in industrial "as-built" applications, historical heritage preservation, architecture, and reverse engineering.
- Triangulation: This method requires a laser emitter and a camera to locate the projection of the laser beam. Both have a constant angle between them, allowing the calculation of the remaining sides of the triangle (using trigonometric calculations) and, consequently, the distance to the scanned object. To apply this methodology, a line laser, one or more cameras, and triangulation software are needed. With the camera at a specific angle relative to the laser and by varying the laser's orientation, the software can reconstruct the desired point cloud. It is a highly precise laser scanner that needs to be very close to the scanned object.
Types of laser scanners based on the collection technique:
- Static Laser Scanner: The equipment is stationary at a point, scanning the area of interest. Each occupied point is called a "scene," and to measure the entire area of interest, multiple scenes are necessary. These scenes are analytically joined by common points, generating the point cloud. They offer advantages in terms of accessibility (using a conventional tripod as support) and positional accuracy (compensators ensure the equipment's verticality).
- Mobile (Mobile Mapping): A bidirectional laser scanner that takes measurements while in motion. To ensure the positioning of the measured point, external sensors such as GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) and an IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) are required. Its operation is similar to airborne equipment, with precision varying depending on multiple sensors, angles, and measured distances. Field data collection is agile, even at low surveying speeds, making it possible to cover large areas. Due to the external sensors, its size is larger than static scanners and can be installed on any mobile vehicle.
4 applications of laser scanning
As you may have noticed, depending on the type of scanner, it can be used for various types of work. Below, we detail the 4 most important applications of the laser scanner:
- Entertainment: Laser scanners, especially 3D scanners, have been incorporated into the entertainment industry in recent years. The use of 3D scanners, for example, has allowed the film industry to save costs when recreating scenes. These instruments can scan a real-world object, such as the Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela, and generate its 3D image for use in a movie. The same applies to the video game industry, where people are scanned to create different characters for games.
- Industrial: The industry uses laser scanners to control the manufacturing dimensions of high-precision components. These parts are scanned, and the scanner returns data, which is then compared to the base model to ensure there are no errors.
- Cultural Heritage or heritage: Leveraging technology to preserve our history is one of the advantages of the digital transformation our society is undergoing. The use of laser scanners to scan monuments, historic buildings, documents, and more allows us to preserve our historical memory and heritage for future generations. An example of this is the Cathedral of Notre Dame, which, thanks to a 3D scan of its structure using a Leica ScanStation P40, can be faithfully reconstructed based on the collected data.
- As-Built Documentation: Closely related to the previous application. Laser scanners allow for precise data collection about the status of a construction or installation. This data can be used to track the evolution of a structure and ensure proper maintenance.
Advantages of using laser scanners
Have you ever found yourself in the middle of a project, nearing a deadline or needing to make progress, and thought that with more (and better) data, you could have made a better proposal?
The most significant advantages of laser scanners are as follows:
- Measurements: With 3D scanning, you avoid re-surveys since you measure everything in one go.
- Non-Intrusive: No operational stops are needed, and you will not interfere with the construction schedule, avoiding inconvenience for both you and your client.
- Office Project: All project information is available for consultation at any time. Have you ever worked with incomplete or erroneous information, or forgotten to consider a detail?
- Safety: Accessing hazardous or hard-to-reach spaces and obtaining complete and rapid measurements is possible.
- Faster BIM Models or CAD Drawings: When you perform laser scanning, you bring the 3D reality into a workspace where you can accurately model its current state.
In addition to being a powerful tool with unlimited applications, point clouds allow for precise measurements of irregular surfaces, uneven heights, and intricate corners for material analysis and calculation.
It is ideal for both indoor and outdoor spaces, as it covers large distances, enabling users to gather data all around the site. It is a perfect tool for planning.
As we have seen, there are different types of laser scanners in the market. Each professional will choose the one that best suits their work circumstances, making this tool highly versatile and adaptable to any type of job. Regarding prices, you can find a 3D scanner at various price points, from affordable options to more expensive ones. It all depends on quality, precision, and the distance you need to measure.
At Global Geosystems and Topotienda, we specialize in various types of 3D scanners. Here, you can find all the models currently available in our online surveying store.
And with that, we conclude our post about the world of laser scanning. Do you have any questions? Would you like us to discuss a specific type of scanner further? Which laser scanner would you recommend?
Send an email to info@global-geosystems.com with your questions or suggestions!









